Ever ordered your favourite gadget online and felt the joy when it arrived on time, perfectly packed, and just as expected? Now picture the opposite: delays, wrong specs, and poor support. This is where the ISO 9001 Requirements help by building a strong Quality Management System (QMS) to ensure consistency and customer satisfaction.
In this blog, we’ll cover the key ISO 9001 Requirements, including documentation, quality policies, objectives, QMS scope, Provider Management, nonconformities, and performance monitoring. We’ll also explain the clause structure and how it helps businesses improve quality and build trust.
Table of Contents
1) What are the Requirements of ISO 9001?
a) Key ISO 9001 Documentation
b) Quality Policy
c) Quality Objectives and Plans
d) Scope of the QMS
e) Control of External Providers
f) Maintenance and Calibration Records
g) Product/Service Requirements and Review Records
h) Customer Property Records
i) Nonconformity Records
j) Performance Monitoring
k) Structure of ISO 9001 Clauses
l) Conclusion
What are the Requirements of ISO 9001?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001 standard asks you to keep documents that show how your work is done. It does not tell you exactly how to do things. You can set up your Quality Management System (QMS) in a way that suits your business.
This means every company can make a Quality Management System (QMS) that works for its own needs. Whether you have a small shop or a big company, ISO 9001 helps you manage your work better, keep quality high, and make your customers happy. Below are the key ISO 9001 documentation and operational requirements:
1) Key ISO 9001 Documentation
Not all documents are mandatory under ISO 9001, but maintaining clear records makes compliance and management much easier. Well-organised records support the effective setup and operation of your Quality Management System (QMS). Below, we outline the key ISO 9001 requirements and explain how to manage them in a straightforward way.
2) Quality Policy
Write a clear statement that reflects your organisation’s commitment to delivering high-quality products or services and continually improving. The policy should align with customer expectations and applicable regulations. Communicate it to all staff so everyone understands and works towards the same quality objectives.
3) Quality Objectives and Plans
Set clear, measurable goals to improve your products or services. Develop straightforward plans, assign responsibilities to the appropriate personnel, and ensure the necessary resources are available. Review these objectives regularly to monitor progress and make improvements where needed.
4) Scope of the QMS
Define what your Quality Management System (QMS) covers within your organisation. This includes the relevant products, services, departments, and locations. A well-defined scope helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures everyone knows what is included.
5) Control of External Providers
Establish a simple process to evaluate, select, and monitor suppliers to ensure they meet your quality standards. Keep records of their performance and review them regularly. This ensures you work with reliable providers and maintain consistent quality.
6) Maintenance and Calibration Records
Keep simple records of all maintenance and calibration activities for any equipment used to measure or monitor your products and processes. Make sure these records show that your equipment meets recognised standards and include details of any approved laboratories used. These records help ensure accurate and reliable results.
7) Product/Service Requirements and Review Records
Write down all the requirements for your products and services, including any updates or changes. Include details like customer feedback, purchase orders, and tender requests. Keeping these records helps maintain quality standards and ensures customer needs are always met.
Elevate your professional auditing capabilities with our ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Training – Join now!
8) Customer Property Records
Maintain clear records of how you handle customer property, including how it is stored, used, and protected. Also, record any damage that happens while it is in your possession. These records show that you take proper care of property that belongs to others.
9) Nonconformity Records
Keep simple records of any problems where products, services, or processes did not meet quality standards. Write down what went wrong, the actions taken to fix it, and how you made sure the issue does not happen again.
10) Performance Monitoring
Monitor and record how effectively your processes are performing. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), monitoring methods, and results. These records help identify areas for improvement and ensure consistent control over operations.
11) Internal Audits
Carry out regular internal audits to check if your Quality Management System (QMS) is working properly. Record all findings, problems, and suggestions for improvement. These audits help you maintain good quality standards.

12) Management Reviews
Senior leaders should review the QMS from time to time to make sure it is effective. Keep records of these meetings, including audit results, progress on quality goals, and plans for further improvements.
13) Preparing for ISO 9001 Certification
You do not need to have every document ready before starting the certification process. The first audit will show you what needs to be improved. However, preparing as many documents as possible in advance makes the process smoother and faster. Being ready shows your organisation’s commitment to Quality Management.
14) Design and Development Inputs Record
When creating products or services, you need to consider many requirements and important details. These inputs can include customer needs, material specifications, or safety standards. Record all these inputs to show that every important factor was considered during the design process.
15) Design and Development Outputs Record
These outputs describe your final product or service in detail. Records may include design drawings, process instructions, and assembly guidelines. Always check that these outputs match the original inputs to ensure everything is correct and aligned.
16) Production/Service Changes
Keep records of any unplanned changes made to products or services. Include details of why the change was made, its impact, and who approved it. This helps maintain quality and transparency in your processes.
17) Product/Service Conformity Evidence
Maintain records showing that your products or services meet all specified requirements. Include the names of the people who checked and approved the release of products or services. This proves that everything delivered meets quality standards.
Learn internal auditing, ensure compliance, and elevate your career with our ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training – Join now!
Structure of ISO 9001 Clauses
The ISO 9001:2015 standard is organised into 11 clauses that guide organisations in building an effective Quality Management System (QMS). These clauses are grouped into two parts: informative clauses and mandatory clauses.
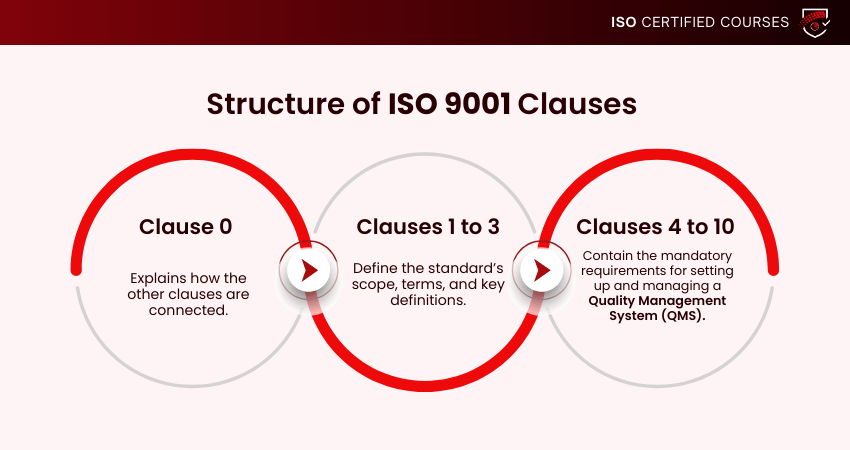
ISO 9001 clauses 0 to 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions
Clause 0 explains the benefits of ISO 9001 and the basics, like:
a) Quality Management System (QMS)
b) Process approach
c) Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle
d) Risk-based thinking
Clauses 1 to 3 include:
a) The scope of ISO 9001
b) References for better understanding
c) Terms and definitions used in the standard
Clause 4: Context of the Organisation
a) Understand your internal and external environment
b) Identify factors that affect your quality goals
c) Know what customers and regulators expect from you
d) Define the scope of your QMS
e) Map and describe the main processes in your organisation
Clause 5: Leadership and Commitment
a) Top management must take the lead in Quality Management
b) Focus on keeping customers satisfied
c) Create and support a clear Quality Policy
d) Designate roles and responsibilities, so everyone knows their duties
Clause 6: Planning for the QMS
a) Identify risks and opportunities that may affect quality
b) Set quality objectives that support the Quality Policy
c) Make plans to achieve these objectives
Clause 7: Support & Resource Management
a) Provide the resources needed to maintain quality
b) Ensure employees are trained and competent
c) Maintain proper infrastructure such as equipment, software, and facilities
d) Create a safe and effective work environment
e) Manage documents, information, and communication properly
Clause 8: Operational Planning and Control
a) Plan and review product and service requirements
b) Handle design and development if applicable
c) Choose and monitor suppliers carefully
d) Control how products are produced, or services are delivered
e) Manage nonconformities to maintain quality
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
a) Monitor and measure how well processes are working
b) Collect and analyse customer feedback
c) Carry out internal audits to check compliance
d) Hold management review meetings to plan improvements
Clause 10: Improvement Actions
a) Find problems and take corrective actions
b) Work on continuous improvement of processes, products, and services
c) Keep updating the QMS to meet changing needs and expectations
Conclusion
The ISO 9001 Requirements provide a clear framework for creating an effective Quality Management System (QMS) that ensures consistency, improves efficiency, and boosts customer satisfaction. Following these guidelines helps organisations manage risks, deliver quality products or services, and build trust, making them stronger and more competitive in the market.
Build a strong foundation for effective Quality Management Systems. Join our ISO 9001 Training now!
Search Smarter
Quickly search through our blog content for what interests you